现在,3D设计不仅在游戏开发中引起了很多关注,而且在网站和下一代界面的世界中也引起了人们的关注。您是否曾经想过:“我想自己创造那个迷人的世界!”?
但是,许多人可能发现3D很困难。现实情况是,使用三js的传统方法直接需要复杂的配置和编写代码,这对初学者来说有点困难。
同时,React三个光纤的使您可以React生态系统中的3D表示此外,打字稿可以提供更安全,更有效的开发。
但是,仍然很少有解释说,即使是初学者也可以不用付出任何努力就可以学习三个纤维和打字稿的组合。
在本文中,我们将解释3D开发的基础知识我们还介绍了使用标准对象(几何和材料)游戏风格的背景和动画
那些新手3D开发的人也可以充满信心地阅读它,因此请务必一起开始。
将来,我们将继续创建课程,并从打字稿x进行三个反应三个光纤!
我们将在YouTube上发布公告,因此请订阅我们的YouTube频道并等待通知!
📺观看YouTube :您可以从此链接
如果您想知道三个纤维可以做什么反应,请参考以下内容!
我们有易于使用的作品!
介绍技术元素:用于此项目的工具和库
您可以将使用的工具和库更改为易于使用的工具和库,但是该项目将解释这一假设。
此外,我们将解释如何在“为打字稿x构建3D环境中用Vite构建3D环境”,因此请检查一下。

- VSCODE
-
- Microsoft提供的免费代码编辑器。
- 它不需要Vscode,但是有很多扩展名,因此我建议它。
- 还建议包括Eslint或更漂亮的。
- node.js
-
- JavaScript建立在Chrome的V8 JavaScript引擎上。
- 您可以在浏览器之外运行JavaScript代码。
- 这是基于已经安装的假设来解释的,因此 https://nodejs.org/ja 下载它
*我们建议下载长期稳定版本的LTS。
- Vite
-
- 现代网络项目的构建工具。它的特征是它的快速和轻巧的
- 先前使用的“ CRA(CREATE-REACT-APP)”未在官方网站上列出,并且已成为旧技术。
- 从现在开始,VITE应该是使用React创建应用程序时的最佳选择。
- 反应
-
- 这是用于构建UI(用户界面)的JavaScript库。它是由Facebook开发的,目前仍在许多Web应用程序中使用。
- 三
-
- JavaScript库,可轻松创建3D图形。它抽象了WebGL的复杂操作,并启用了直观的3D开发。
- 与Direct WebGL操作相比,创建3D图形很容易使用,并且更易于使用。
- 反应三个纤维
-
- 这是一个允许将三个.js用于React的库。它将React的组件结构与三个JS的3D发动机相结合。
- 三个JS可以在反应开发方式中使用,从而可以进行直观有效的发展。
- 反应三个drei
-
- 用于三个纤维的有用实用程序组件的集合。添加常用的三个JS功能很容易。
- 可以通过简短的代码来实现复杂的3.JS功能,从而降低学习成本。
网眼
要绘制3D对象,请使用网格组件。
网格由几何和材料组成。
存在属性,例如位置,旋转,比例,castshadow和receiveshadow。
您还可以定义诸如OnClick之类的事件。有关更多信息,请参阅三个文档。
函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh position={[0, 1, 0]} // 位置 rotation={[Math.PI / 4, 0, 0]} // 回転(ラジアン) scale={[2, 2, 2]} // スケール(拡大) castShadow // 影を投げる receiveShadow // 影を受け取る ><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="red" /></mesh></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;几何学
什么是几何?
几何定义了组成对象的顶点,边缘和面的位置,大小和连接性。
- 顶点(蓝色):它们是定义对象形状的3D空间中的个别点。每个顶点的坐标(X,Y,Z)确定其在3D空间中的位置。顶点在边缘连接以形成脸部
- 边缘(绿色):边缘是连接顶点的线。这些定义了物体的形状,并且可以直接或弯曲。每个边缘都由一组指向顶点的索引组成。
- 脸(黄色):面孔是由连接顶点形成的多边形。面部定义物体的表面,可以是三角形,正方形或其他多边形。每张脸也包括一组指向顶点的索引。
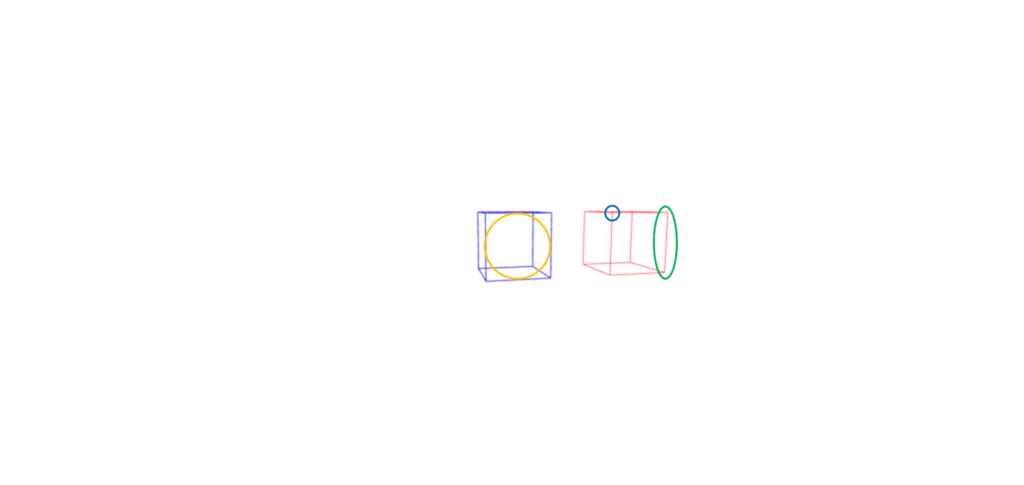
几何类型
反应三个纤维(3.Js)具有很多现成的几何形状。
以下是一些最常见的。
票日测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><boxGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

球体测量法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><sphereGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
平面测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><planeGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
圆地测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><circleGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
气缸测量法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><cylinderGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
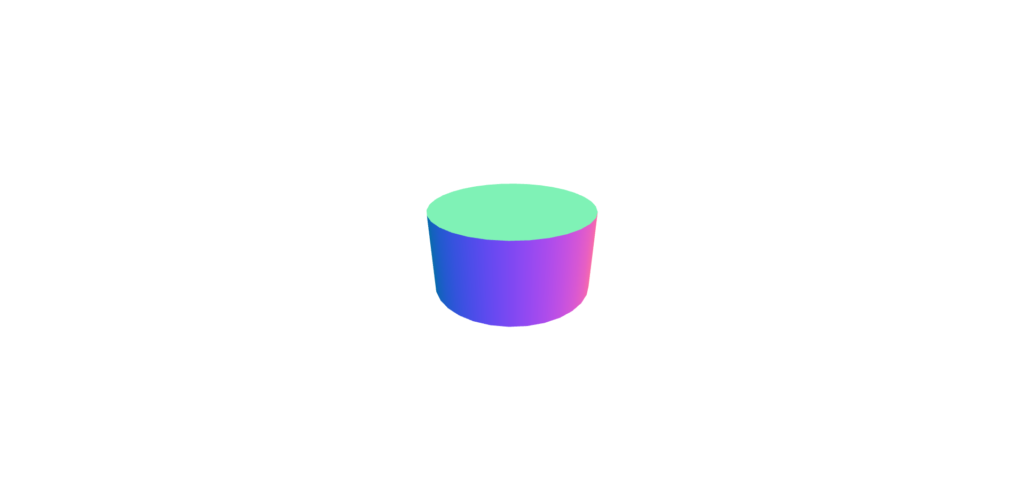

胶囊测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><capsuleGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

圆锥体计
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><coneGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

十二面体的测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><dodecahedronGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

挤出测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><extrudeGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

Icosahedrongemetry
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><icosahedronGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
载层
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><latheGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
八面体的测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><octahedronGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
多面体测量法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数app():jsx.element {const vertices = [0,0,1,// vertex 1 0,1,0,// vertex 2 1,0,0,0, // vertex 3 -1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,// vertex 4]; const indices = [0,1,2,// face 1 0,1,3,// face 2 0,2,3,// face 3 1,2,3,// face 4];返回 ( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><polyhedronGeometry args={[vertices, indices, 1, 0]} /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

四面体组
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><tetrahedronGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

曲线测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
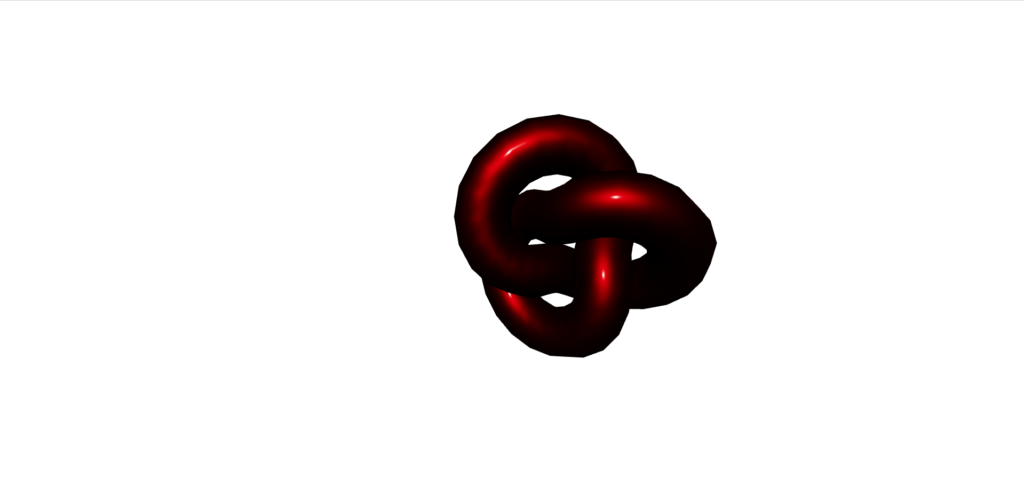
曲线旋转的测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

管道测定法
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><tubeGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;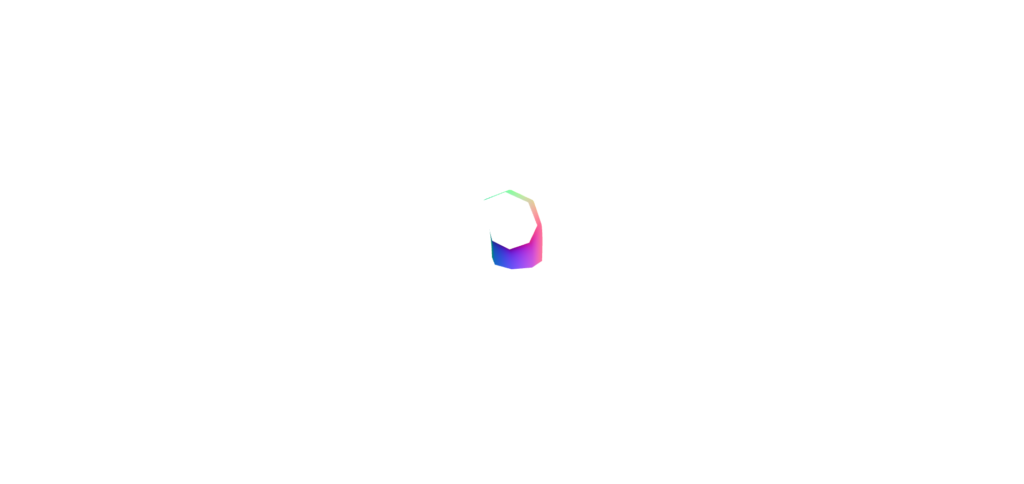
铃声
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><ringGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
形状测定法
从“三”导入{shape,vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数app():jsx.element {const shape = new Shape(); //定义心形形状。Moveto(0,0.5); Shape.BezierCurveto(0.5、1、1、0.5、0、0); Shape.BezierCurveto(-1,0.5,-0.5,1,0,0.5);返回 ( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><shapeGeometry args={[shape]} /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

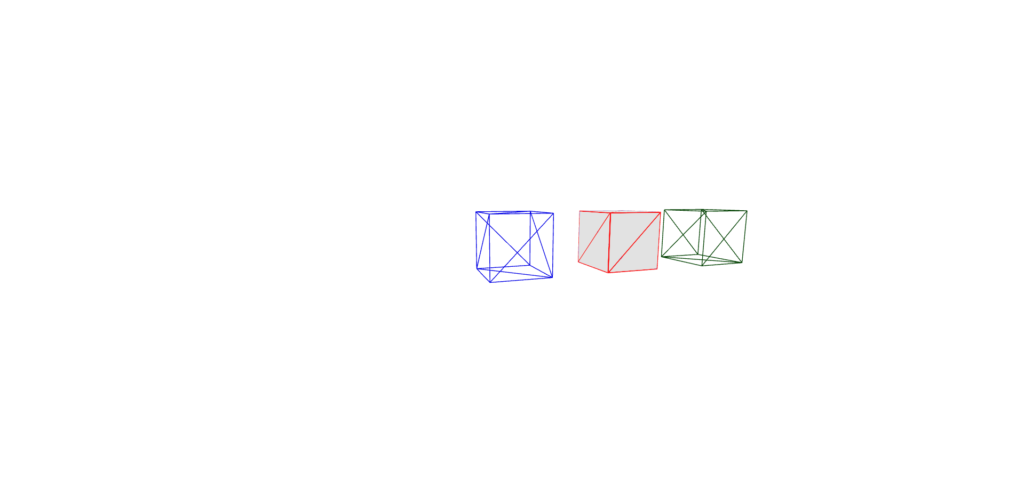
边缘测定法
从“三”导入{vector3,boxesememetry};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{edges,meshdiscardmaterial,orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}> {/ *仅3纤维 */} <lineSegments><edgesGeometry args={[new BoxGeometry(1)]} /><lineBasicMaterial color="blue" /></lineSegments> {/ * react-three-drii */} <mesh position={[2, 0, 0]}><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><MeshDiscardMaterial /><Edges color="red" /></mesh><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
如果仅使用Ereact三纤维的边缘,则需要直接使用三个。
另一方面,React-Three-Drei允许您简单地写入而无需直接使用三个JS,但是React-three-Drei的边缘也绘制面孔,因此您需要使用MeshdiscardMaterial
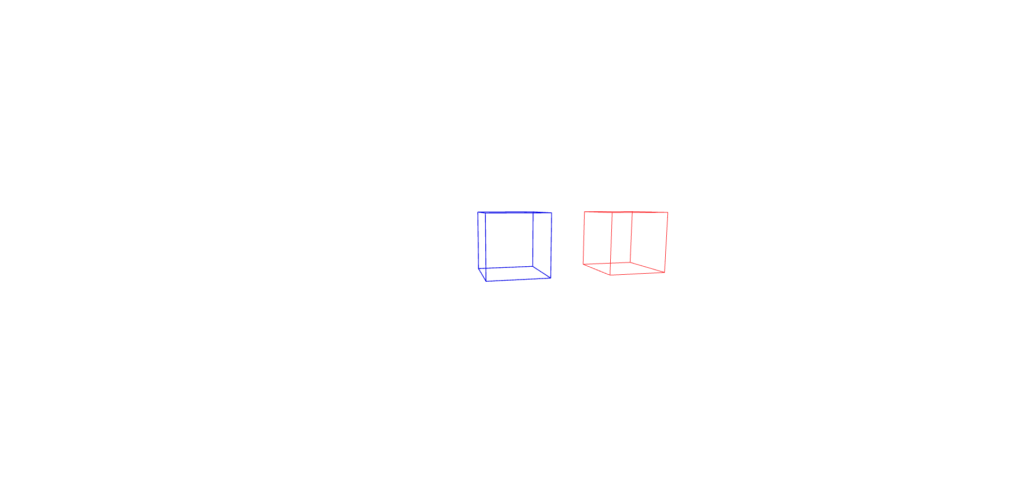
线框测定法
从“三”导入{vector3,boxesememetry};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls,线框}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}> {/ * React-三纤维 */} <lineSegments><wireframeGeometry args={[new BoxGeometry(1)]} /><lineBasicMaterial color="blue" /></lineSegments> {/ * react-three-drii */}<mesh position={[2, 0, 0]}><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><Wireframe stroke="red" /></mesh> {/ *另一种解决三纤维的解决方案 */} <mesh position={[4, 0, 0]}><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="green" wireframe /></mesh><OrbitControls /><ambientLight /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
一个称为线框的反应三个DRII组件也绘制面孔。
另一种反应三纤维的解决方案可能是最容易使用的方法。
材料
材料定义了确定材料确定对象表面绘制时的外观的信息。
存在属性,例如对象颜色,纹理,透明度和反射率。
要检查材料,您需要一盏灯。我将在另一个场合解释有关灯的信息,所以这次请在以下内容中包含环境光和定向灯。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /> //添加灯光<directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} />//添加灯光<OrbitControls /></Canvas>); }导出默认应用程序;
反应三个纤维中的材料类型(3.JS)
反应三个纤维(3.JS)具有许多预制材料。
以下是一些最常见的。
meshbasicmaterial
meshbasicmaterial是一种不受光源影响的简单材料。显示纹理和颜色。
它通常用于线框,非实时渲染,背景等。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshBasicMaterial color="red" /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
网状材料
网状材料是一种特殊材料,可视化顶点和表面的正态。这也不受光的影响。
它通常用于调试目的,以检查模型的结构和正态是否正确。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

Meshlambertmaterial
Meshlambertmaterial是一种仅具有分散反射的轻质材料。它计算弥漫性反射并创建哑光外观。这是轻巧的,但不现实。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshLambertMaterial color="red" /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

meshphongmaterial
除了兰伯特的性质外,Meshphongmaterial是一种具有镜面反射的材料。可以表达镜面反射,但这也不是现实。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshPhongMaterial color="red" shininess={100} /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
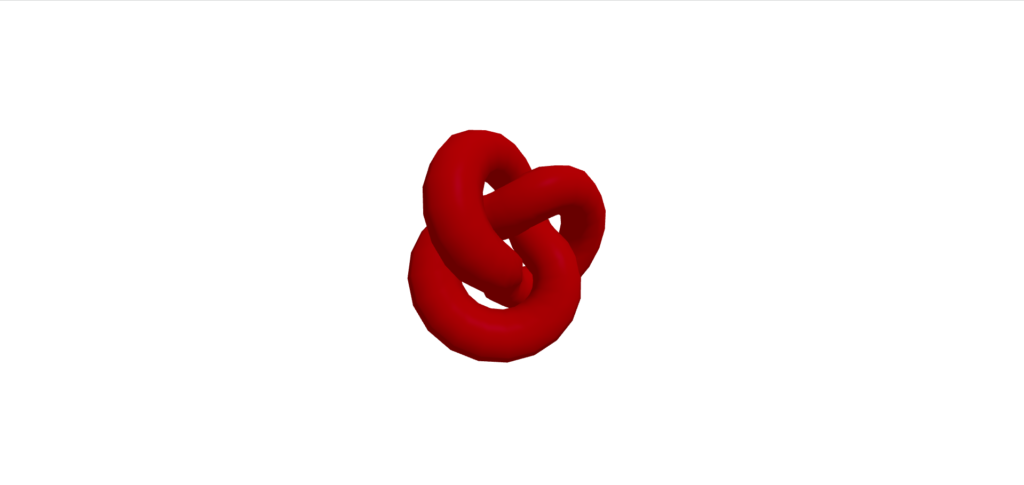
网格标准材料
MeshStandardMaterial是一种支持PBR(基于物理渲染)的材料。重现逼真的光反射和阴影。您可以设置金属和粗糙度,从而创造出相当逼真的纹理。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshStandardMaterial color="red" metalness={1} roughness={0.5} /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

网状物理材料
网状物质材料是网格标准材料的扩展
已经添加了高级物理特性,例如传输,反射率和透明外套。可以表达传播和折射,例如玻璃或水滴。它使得可以更现实地表达,但也需要更多的计算工作。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshPhysicalMaterial color="red" metalness={1} // 金属感を最大に roughness={0.5} // 表面の粗さ(滑らか) clearcoat={0.8} // 反射の強さ clearcoatRoughness={0.1} // 反射面の粗さ /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

| 特征 | Meshlambertmaterial | meshphongmaterial | 网格标准材料 | 网状物理材料 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阴影模型 | 兰伯特阴影 | fon阴影 | 基于物理的阴影(PBR) | 基于物理的阴影(PBR) |
| 金属感觉 | 没有任何 | 没有任何 | 金属表达金属感觉 | 金属表达金属感觉 |
| 粗糙度 | 没有任何 | 没有任何 | 表面粗糙度与粗糙度 | 表面粗糙度与粗糙度 |
| 反射 | 没有任何 | 镜面反射(光泽) | 可能的简单反射 | 用透明 |
| 透明度和折射 | 没有任何 | 没有任何 | 没有任何 | 使用透明度和屈光度 |
| 表现 | 高速 | 有点晚了 | 有点沉重 | 最重(管理密集型) |
| 使用的目的 | 简单的场景,面向性能 | 闪亮的表面(塑料,金属) | 需要逼真的身体表达的场景 | 需要逼真的反射,折射,金属感觉和透明的场景 |
| 特征 | 简单的弥散反射 | 扩散和镜面反射(亮点) | 物理上准确的反射,弥漫性反射,金属感觉,粗糙度 | 物理上准确的反射,透明度,折射,金属感觉 |
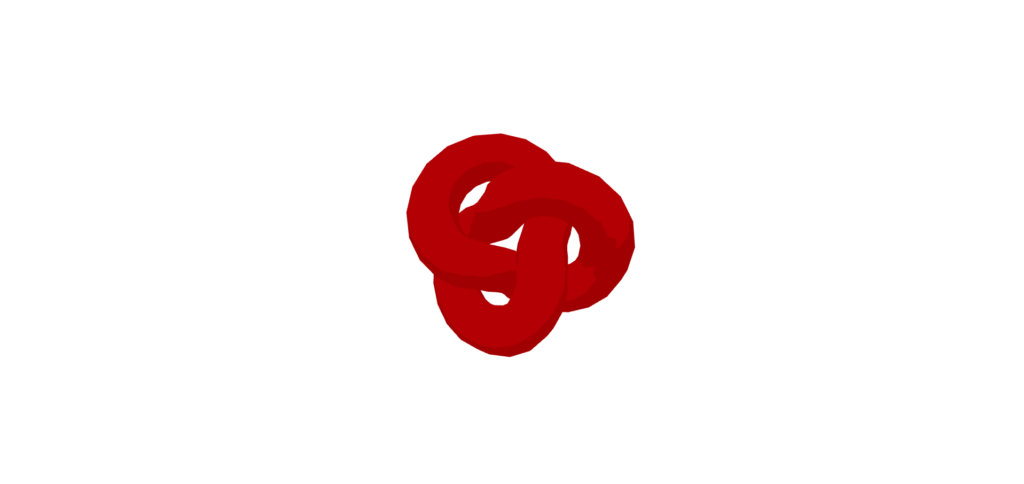
MeshtoonMaterial
MeshtoonMaterial是一种具有动画风格的台阶式阴影的材料。它并没有实现,而是通常用来表达卡通风格。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshToonMaterial color="red" /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

网格材料
网格材料是一种根据深度改变颜色的特殊材料。从对象到相机的距离以颜色表示。这也不受光的影响。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshDepthMaterial /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
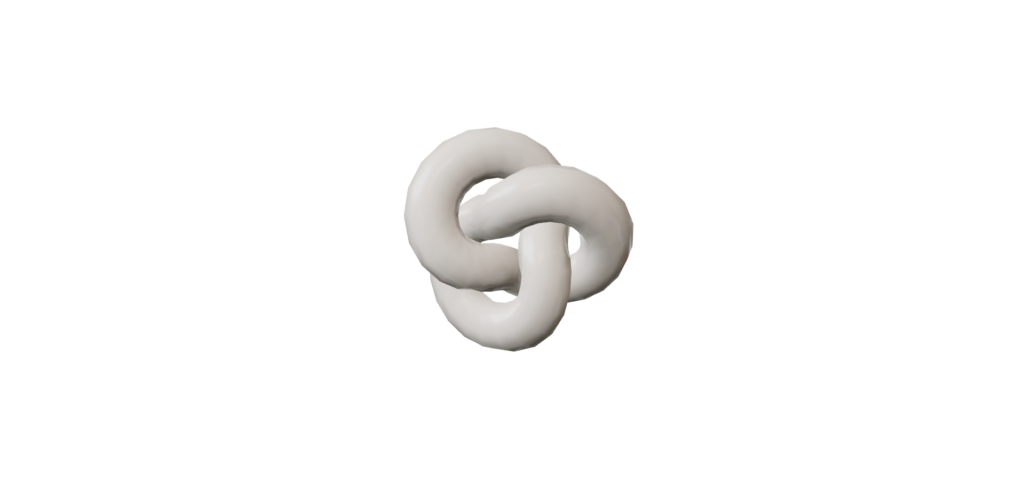
meshmatcapmaterial
meshmatcapmaterial是一种使用2D纹理(MATCAP)来重现逼真阴影的材料,而无需考虑光源。
该图像包含光信息,使创建现实表达式成为可能。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”中导入{canvas,useloader};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls};从“三”导入{textureloader}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:JSX.Element {//带有纹理加载器const Matcaptexture = useloader(textUreLoader,“ https://threejs.org/examples/texamples/textures/matcaps/matcap-/matcap-porcelain-white-white.jpg”)返回 ( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><meshMatcapMaterial matcap={matcapTexture} /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;

反应三个drei中的材料类型
React Three DREI提供了更高级的材料。
网格材料
MeshdiscardMaterial是一种没有任何东西的材料。您可以从场景中隐藏对象,同时仍显示阴影和孩子。
从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{meshdiscardMaterial,orbitControls};从“三”导入{vector3}; const initial_camera_position = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas shadows camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }} style={{ background: "lightblue" }} ><mesh castShadow receiveShadow><torusKnotGeometry /><MeshDiscardMaterial /></mesh> {/ *地面(尖锐的阴影) */} <mesh receiveShadow position={[0, -1.8, 0]} rotation={[-Math.PI / 2, 0, 0]} ><planeGeometry args={[5, 5]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="lightgray" /></mesh> {/ *照明设置 */} <ambientLight intensity={0.3} /><directionalLight position={[5, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} castShadow shadow-mapSize-width={1024} shadow-mapSize-height={1024} /> {/ *相机操作 */}<OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;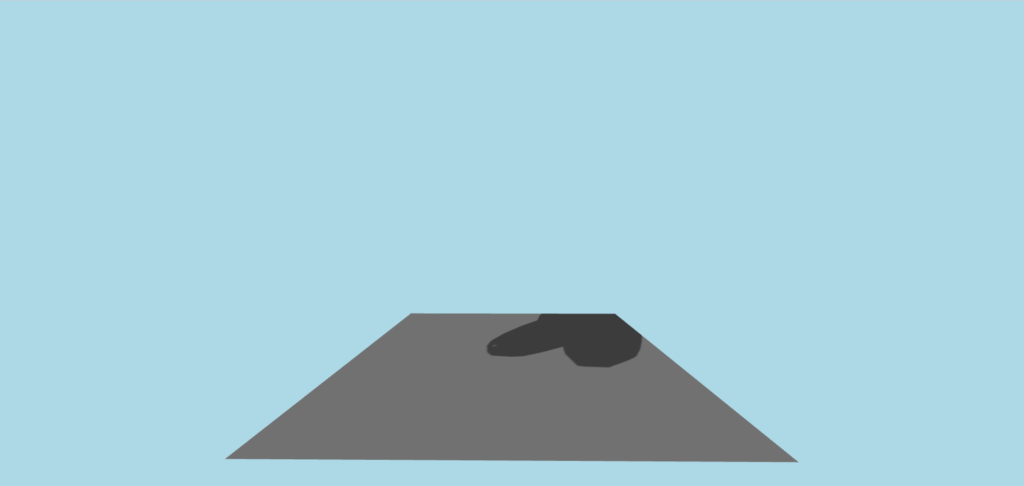
网状材料
网状材料是一种可能扭曲几何形状的材料。它不仅具有颜色和纹理,还具有运动的特征。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{meshdistortMaterial,orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><MeshDistortMaterial distort={1} speed={10} /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;网状质材料
网眼材料是一种材料,可让您轻松地在网格中添加反射和模糊。网格标准材料扩展使创建类似镜像的表达变得更加容易。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{meshdistortMaterial,meshRefreformaterial,orbitControls,orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><MeshDistortMaterial distort={1} speed={10} /></mesh> {/ *反射表面(地面) */} <mesh rotation-x={-Math.PI / 2} position={[0, -3, 0]}><planeGeometry args={[10, 10]} /><MeshReflectorMaterial blur={[200, 100]} // X, Y方向のぼかしを設定 mixBlur={0.5} // ぼかしの強さを調整 mixStrength={0.7} // 反射の強さ mixContrast={1} // 反射のコントラストを調整 resolution={512} // 解像度、値を上げるほどきれいになるがパフォーマンスに影響 mirror={1} // 環境から反射を取得 depthScale={0.1} // 深さのスケール reflectorOffset={0.2} // 反射面のオフセット /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
Meshtransmissionmaterial
MeshtransmissionMaterial是一种改进的网状物质材料。它旨在使其更容易处理变速箱和折射。主要功能是设置IOR
IOR(折射索引) :这是一个数字,代表光线通过材料传播的速度与在空气中行驶的速度之间的比例,并且当易于设置这一速度时,它变得非常容易描述玻璃,钻石,水等。
- 空气IOR:1.0
- 玻璃IOR:1.5
- 钻石IOR:2.42
- 水IOR:1.33
从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};导入{clastics,meshtransmatermissmaterial,orbitControls,}来自“@react-three/drei”;从“三”导入{vector3}; //初始相机位置const intire_camera_position = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas shadows camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION, fov: 45 }}><color attach="background" args={["#f0f0f0"]} /><Caustics color="#FF8F20" position={[0, -0.5, 0]} lightSource={[5, 5, -10]} worldRadius={0.01} ior={1.2} intensity={0.005} causticsOnly={false} backside={false} ><mesh castShadow receiveShadow position={[-2, 0.5, -1]} scale={0.5}><sphereGeometry args={[1, 64, 64]} /><MeshTransmissionMaterial resolution={1024} distortion={0.25} color="#FF8F20" thickness={1} anisotropy={1} /></mesh></Caustics><mesh><boxGeometry /><meshNormalMaterial /></mesh> {/ *照明设置 */}<ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /> {/ *相机操作 */}<OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
网格揭示
网络Wobblemberatial是一种可以摇动和波浪形几何形状的材料。这也是可以应用于运动的材料。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{meshwobblecterial,orbitControls}; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh><torusKnotGeometry /><MeshWobbleMaterial factor={1} speed={10} /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
软胸罩
SoftShadows是一个组件,使添加更真实的阴影变得更加容易,尽管这不是材料。您将能够轻松地表达阴影的阴影。
从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{softshadows,orbitControls};从“三”导入{vector3}; const initial_camera_position = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return(<Canvas shadows camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }} style={{ background: "lightblue" }} >{/ *启用SoftShadows */} <SoftShadows /><mesh castShadow receiveShadow><torusKnotGeometry /><meshStandardMaterial color="red" /></mesh> {/ *地面(尖锐的阴影) */} <mesh receiveShadow position={[0, -1.8, 0]} rotation={[-Math.PI / 2, 0, 0]} ><planeGeometry args={[5, 5]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="lightgray" /></mesh> {/ *照明设置 */} <ambientLight intensity={0.3} /><directionalLight position={[5, 5, 5]} intensity={0.7} castShadow shadow-mapSize-width={1024} shadow-mapSize-height={1024} /> {/ *相机操作 */}<OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;这有点令人困惑,但是与前面提到的MeshdiscardMaterial的阴影相比,可能更容易理解。

关于材料的前后
材料的一侧定义了渲染的一侧。
默认情况下,它是前边,但是您也可以通过设置背面呈现背面。
从“三”导入{vector3};从“@react-three/fiber”导入{canvas};从“@react-three/drei”中导入{orbitControls};从“三”中导入 *为三个; //常量const initial_camera_position:vector3 = new vector3(3,3,3);函数应用程序:jsx.element {return(return( <Canvas camera={{ position: INITIAL_CAMERA_POSITION }}><mesh position={[0, 0, 0]}><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="red" side={THREE.FrontSide} // Optional as it's the default /></mesh><mesh position={[2, 0, 0]}><boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} /><meshStandardMaterial color="red" side={THREE.BackSide} // Optional as it's the default /></mesh><ambientLight intensity={0.5} /><directionalLight position={[0, 3, 3]} intensity={0.7} /><OrbitControls /></Canvas> ); }导出默认应用程序;
使用标准几何和材料创建3D内容
使用标准的几何形状和React三纤维的材料创建简单,有趣的交互式3D内容,并反应三个DREI。
登录屏幕(游戏样式)
我已经复制了屏幕以选择一个oke poke包并对其进行定制!
我创建的3D背景就像
📺在YouTube上观看演示:链接中观看


如果您发现这有用,请订阅我们的频道!
将来,我们将继续创建课程,并从打字稿x进行三个反应三个光纤!
我们将在YouTube上发布公告,因此请订阅我们的YouTube频道并等待通知!
📺观看YouTube :您可以从此链接
如果您想知道三个纤维可以做什么反应,请参考以下内容!
我们有易于使用的作品!


![如何构建一个自动在Chatgpt + Next.js [OpenAI API + NEXT.JS + Tailwind CSS]中自动生成LP的Web应用程序]](https://hack-lab-256.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/hack-lab-256-samnail-27-300x169.jpg)

![我尝试使用OpenAI API [Next.js + Tailwind CSS]创建聊天机器人](https://hack-lab-256.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/hack-lab-256-samnail-25-300x169.jpg)

![[对于初学者]介绍三个光纤X DREI X打字稿!从图像创建像素艺术和动态动画](https://hack-lab-256.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/hack-lab-256-samnail-16-300x169.jpg)
![[完整说明]用React三个光纤×打字稿学习! 3D对象转换(位置,旋转,比例)的实用指南](https://hack-lab-256.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/hack-lab-256-samnail-15-300x169.png)